Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the symptoms and treatment of which are diverse, is one of the most common pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
This condition is characterized by the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs, spreading over time to the ligaments and bone tissue of the vertebrae of the lumbosacral spine. An acute process, against the background of a lack of therapy, inevitably turns into a chronic one.
Degenerative disease can turn a healthy person into a disabled person.
Degrees of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Classify 4 degrees of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region. The scheme of the development of the disease is as follows:
First degree.In the inner part of the annulus fibrosus, lesions in the form of cracks are formed, where the contents of the nucleus pulposus penetrate, causing irritation. This is the initial stage of osteochondrosis. The deformation of the intervertebral discs is barely pronounced and gives reflex pain with sudden movements and heavy lifting. Unpleasant sensations in the lower spine can be mild and manifest:

- lumbodynia - local, lasting pain in the lumbar spine;
- lumbago - sudden painful "lumbago" in the lower back.
Second degree.The destructive processes in the fibrous ring continue. The distance from one vertebra to another decreases, causing compression of the nerve fibers. There is discomfort in the lower third of the back, which at times develops into bouts of pain.
Third degree.During this period, the final destruction of the annulus fibrosus occurs with the extrusion of the nucleus pulposus. Vessels and nerve endings are compressed by intervertebral discs. An intervertebral hernia is formed. The spine is curved, forming:
- lordosis - an arcuate deformity in the lumbar spine, with a forward bulge of the spinal column;
- kyphosis - the position opposite to lordosis, when the arc forms outward;
- scoliosis - pathological bending of the spine to the right or left.
The last degreeosteochondrosis is considered the most severe and dangerous. At this time, the spine is already deformed, normal motor activity is lost. X-rays show bony growths in the lumbar spine - the body's response. Pain may be absent for a while, but this does not mean improvement. People suffering from stage 4 osteochondrosis of the sacro-lumbar spine often become disabled. The reason is that at this stage the process is complicated.
Causes of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Among the causes of lumbar osteochondrosis are the following:
- Disproportionate load on the spine.Man is an erect creature, therefore, in a standing position, the load on the spinal column is considered normal. When performing various actions, you have to move, bending and unbending. To maintain the body in the desired condition, the musculoskeletal system is in a mode of prolonged tension. In the sitting position, the load on the spinal column increases, and when lying on the back, it becomes minimal. When a person is in one position for a long time, the lumbar and sacral parts of the spine are overloaded and the muscles do not rest, from which there is first a feeling of discomfort, and then pain. This deforming factor creates the preconditions for the development of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
- Sedentary lifestyle.It contributes to the development of various pathologies, including those that affect the vertebral structures. Prolonged sitting causes deformation of the cartilage tissue and a decrease in muscle tone, provoking the development of lumbar osteochondrosis.
- Excessive physical exertion.Both the lack of vigorous physical activity and its excess do not bring anything good for the musculoskeletal system. Long, hard work, especially associated with lifting and carrying weights, leads to overstrain of the back muscles and causes the formation of vertebral hernias.
- Posture disorders.Deformation of the discs between the vertebrae can also be caused by improper walking. The reason is again in the uneven load on the spinal column. Intervertebral discs lose elasticity, mobility, and therefore are more likely to be damaged. More than others, people of older and older age suffer from similar problems.
- Bone defects, hereditary pathologies, trauma and infectious lesions.Often, osteochondrosis is a consequence of disorders of the musculoskeletal system that were present at birth. For example, when the cartilage tissues of the body are naturally fragile. In addition, pathologies of the spine develop after traumatic injuries and infectious processes, as in osteomyelitis and tuberculosis.
- Flat feet.Signs of a "special" foot - the absence of a notch and drooping of its arches. Those who have such a feature often face spinal problems. This is due to the increased load on the intervertebral discs when walking. Throughout life, they are subject to increased physical stress during movement, therefore they wear out quickly
- Obesity.Excess weight is a problem and an additional burden for the body. All organs and systems suffer, including the spine.
- Pathological processes.Dysfunctions of various structures can adversely affect the condition of the musculoskeletal system. So the factors that provoke osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine are endocrine disorders, cardiovascular problems and malfunction of the digestive system.
- Wrong way of life.Many people do not pay enough attention to such simple and important things as physical activity, balanced nutrition and normal sleep. An organism that exists for a long time under stress conditions becomes weakened and vulnerable. Among other pathologies that can arise on such a "fertile" soil, includes lumbar osteochondrosis.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
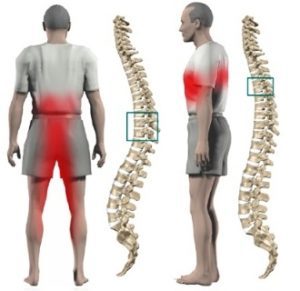
Pathological changes in the lumbar spine are manifested by severe symptoms;
- Lower back painis the clearest "signal" of the development of lumbar osteochondrosis. She speaks of the presence of "radicular syndrome", when compression of the nerve endings of the spine causes pain in the lumbar region. The person becomes tired and irritable. Over time, doing simple and routine activities becomes a big problem due to pain in the lumbar spine. If an intervertebral hernia has formed in the lumbar region, the pain radiates to the lower leg, back of the thigh and foot. Over time, it becomes more and more difficult to sit and walk. Unpleasant sensations do not let go even when lying down. Temporary relief may alternate with periods of exacerbation . ;
- dysfunction of the genitourinary system.They are manifested by pain in the kidney area, frequent urge to urinate. Deformation of the intervertebral discs causes displacement of the lumbar spine relative to the sacrum. This affects the work of the internal reproductive organs in women, and in men it causes problems with potency;
- decreased sensitivity of the legs in the area of the foot.It can be either partial or absolute. At the same time, the reflexes of this part of the body are weakened. Progressive pathology leads to a complete loss of sensitivity of the lower extremities;
- gait disturbances. Pain in the lumbar spine with osteochondrosis makes a person when walking to deviate in the direction opposite to that where the nerve fibers are pinched. The condition does not allow walking long distances. A lame person is forced to stop from time to time, expecting pain relief. Timely medical assistance can save a person from disability.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
Many people are wondering whether osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is treated and how it happens. When the diagnosis is made and the diagnosis is made, the therapeutic tactics are determined.
There are various methods by which lumbar osteochondrosis is treated. Which of them is necessary and advisable to apply in order to cure a disease or alleviate a person's condition as much as possible, the doctor determines.
Someone treats themselves exclusively with folk remedies, at home, forgetting that they can be used only with the approval of a medical specialist and only as part of complex therapy.
Medication for osteochondrosis
Drug therapy involves the use of:
- tablet forms;
- injection solutions;
- preparations for external use - ointments and gels.
Medications are prescribed that eliminate inflammation and relieve pain in the lumbar spine. They can be used at home.
These could be:
- analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- drugs for muscle spasms (muscle relaxants);
- means for restoring cartilage tissue (chondroprotectors);
- corticosteroids (hormone-containing drugs that act to relieve pain and inflammation)
- vitamins.
The course of treatment is prescribed by a doctor, who sometimes prescribes pills or potions to calm the nervous system as an additional treatment.
Physiotherapy for lumbar osteochondrosis
Physiotherapy is another common method for relieving the symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis. Acting on the spine and lower back, it enhances metabolic and restorative processes.
Most often prescribed:
- magnetic, laser and electrotherapy;
- phonophoresis;
- shock wave method;
- detensor therapy;
- vibration massage;
- balneotherapy.
How many and what procedures will be required - the doctor decides.
Physiotherapy is effective when it comes to the initial stages of pathology. But she, like other types of treatment, has contraindications. Therefore, when prescribing this method, the doctor takes into account many factors.
Therapeutic gymnastics for lumbar osteochondrosis
A set of physical exercises that can be shown for lumbar osteochondrosis is aimed at restoring the mobility of this spine.
Regularity is considered the main condition for its effectiveness. Exercises performed occasionally will not bring the desired effect.
If the body already has complications caused by osteochondrosis, this method is not applied. In addition, contraindications to its use are severe pathologies of other organs and systems, as well as the presence of pain in the pelvic region and above.
Surgical intervention for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
The surgical method is used in the presence of such severe complications as an intervertebral hernia. Partial or complete removal of the damaged intervertebral disc (discectomy) is performed, as provided by the operation protocol.
The indications for surgery are:
- strong and persistent pain syndrome, which cannot be removed with medication for a month;
- the large size of the hernia and its effect on the spinal cord.
Osteochondrosis is easier to prevent than to cure. Like any pathology, it is potentially dangerous with severe complications. It is important to understand that more or less complete disposal of this pathology is possible at the earliest stages, when the deforming effect on the intervertebral discs is minimal. In other cases, we can only talk about relieving symptoms and maintaining the state of the body, which allows you to live and work normally.












































